Potassium Dichromate Colour Change
Test for Sulphite ion SO2 3 a On treating sulphite with warm dil. COD can be measured in rapidly or in real-time with Real Techs COD instruments to improve wastewater process control and plant efficiency.

Potassium Dichromate Test For Alcohols Stock Image C040 2657 Science Photo Library
If the potassium dichromate solution changes colour from orange to green then an oxidation reaction has taken place with a primary or secondary alcohol.
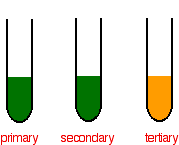
. These change colour in the presence of an oxidising agent. Energy barrier built-up when the collision is about to take place Activated complex formation difference in energy of the reactant and the product Actinoidsexothermic and endothermic reactions with proper graphs and labelling. A redblue oscillating reaction.
Unlike permanganate dichromate titrations require an indicator. When the solution of K 2 Cr 2 O 7 reacts with an alkali ionic salt a yellow solution is obtained because of the. Mohrs salt Titration with Potassium Dichromate.
There are several such indicators - such as diphenylamine sulphonate. Includes kit list and safety instructions. This is often seen in redox titrations for instance when the different oxidation states of the product and reactant produce different colours.
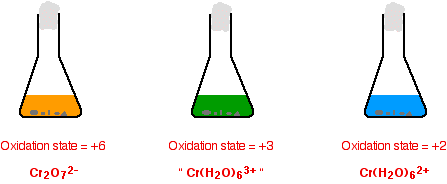
It is maintained with the use of dilute sulphuric acid. The color of chemicals is a physical property of chemicals that in most cases comes from the excitation of electrons due to an absorption of energy performed by the chemical. In the potassium dichromate solution Cr 2 O 7 2-ions in orange colour are in equilibrium with CrO 4 2-ions in yellow colour.
Tollens reagent or Fehlings solution can then be used to. Here is the equation. In this type of titration the strength of a solution is determined by its complete precipitation with a standard solution of.
Change close contact particles should collide. This colour change of orange to yellow and yellow to orange can be explained on the concept of equilibrium of the two ions. These are diphenylamine diphenylbenzidine and diphenylamine sulfonate.
Sodium nitroprusside Complex of Purple colour 3. There are three indicators that may be used for the titration of Fe 2 with K 2 Cr 2 O 7. Butanol is oxidised by sodium dichromate Na 2 Cr 2 O 7 acidified in dilute sulphuric acid to form the aldehyde butanal.
After that add 5 ml of concentrated nitric acid. The colour change for all three indicators is green to violet and the standard electrode potentials are all ca 078 V. In this the brown colour will not change into blue.
H 2 SO 4 SO 2 gas is evolved which is suffocating with the smell of bur ning sulphur. The Mohr titration is sensitive to the presence of both chloride and bromide ions in solution and. Cr 2 O 7 2- H 2 O 2CrO 4 2- 2H Orange-red Yellow.
With potassium dichromateVI solution you have to use a separate. H 2 SO 4 green. Chemical Oxygen Demand or COD is a measurement of the oxygen required to oxidize soluble and particulate organic matter in water.
Aim To prepare M20 solution of Mohrs salt and using this solution find out the molarity and strength of the given potassium permanganate KMnO 4 solution. Using potassium dichromateVI solution. Collisions to be effective optimum energy and proper orientation during collision.
Chemical Properties of Potassium Dichromate. What is seen by the eye is not the color absorbed but the complementary color from the removal of the absorbed wavelengthsThis spectral perspective was first noted in atomic spectroscopy. Then add a few drops of 5 potassium dichromate solution.
Use this practical to investigate the oxidation reactions of various alcohols with acidified potassium dichromate. Use this practical or demonstration to provide a visual illustration of an oscillating reaction and redox equilibria. Na 2 SO 3 H 2 SO 4 Na 2 SO 4 H 2 O SO 2 The gas turns potassium dichromate paper acidified with dil.
In this titration the potassium permanganate is used as an oxidizing agent. Includes kit list and safety instructions. 2KMnO 4 3H 2 SO 4 K 2 SO 4 2MnSO 4 3H 2 O 5O Or MnO 4 8H 5e Mn 2 4H 2 O.
Reaction to form hydrogen chromate ions or dichromate ions affecting the accuracy of the end point. Introducing heat to K 2 Cr 2 O 7 decomposes it into potassium chromate K 2 CrO 4 and produces O 2 gas. If no colour change is observed then the alcohol was a tertiary alcohol.
A primary alcohol will form an aldehyde and a secondary alcohol will form a ketone. If the colour of the solution changes from brown to blue it indicates glycerol. Theory Redox titrations are those titrations in which a reducing agent is titrated against the oxidising agent or oxidising agent is titrated against a.
Tests for the Free. Potassium dichromateVI solution turns green as it reacts with the ironII ions and there is no way you could possibly detect the colour change when you have one drop of excess orange solution in a strongly coloured green solution. The oxidation of the alcohol to an aldehyde is indicated by the colour change of the dichromate solution as it is reduced from the orange colour of Cr 2 O 7 2 to the green of chromiumIII ions Cr 3.
The end point of a potassium dichromateVI. It is a good idea to first carry out a rough titration in order to become familiar with the colour change at the end point. In some reactions the solution changes colour without any added indicator.
K 2 Cr. In association with Nuffield Foundation. However the colour is made difficult by the strong green also present.
4K 2 Cr 2 O 7 4K 2 CrO 4 2Cr 2 O 3 3O 2. Observe the test tube for the appearance of a blue colour. This gives a violet-blue colour in the presence of excess potassium dichromateVI solution.
Iodimetric and Iodometric Titrations.
Content Redox Chemistry Inside The Breathalyzer The Alcohol Pharmacology Education Partnership

The Colour Change Of Acidified Potassium Dichromate The Real Chemist Youtube
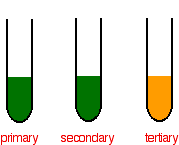
14 7 Determining Alcohol Classifications In The Lab Alternate Reactions Chemistry Libretexts
Comments
Post a Comment